How to Create Your Own Search Engine: What You Must Consider

The user usually does not have exhaustive knowledge about the information content of the resource in which he conducts the search. To assess the adequacy of the query expression, as well as the completeness of the result obtained, he can find additional information, or organize the process so that part of the search results can be used to confirm or deny the adequacy of the other part.
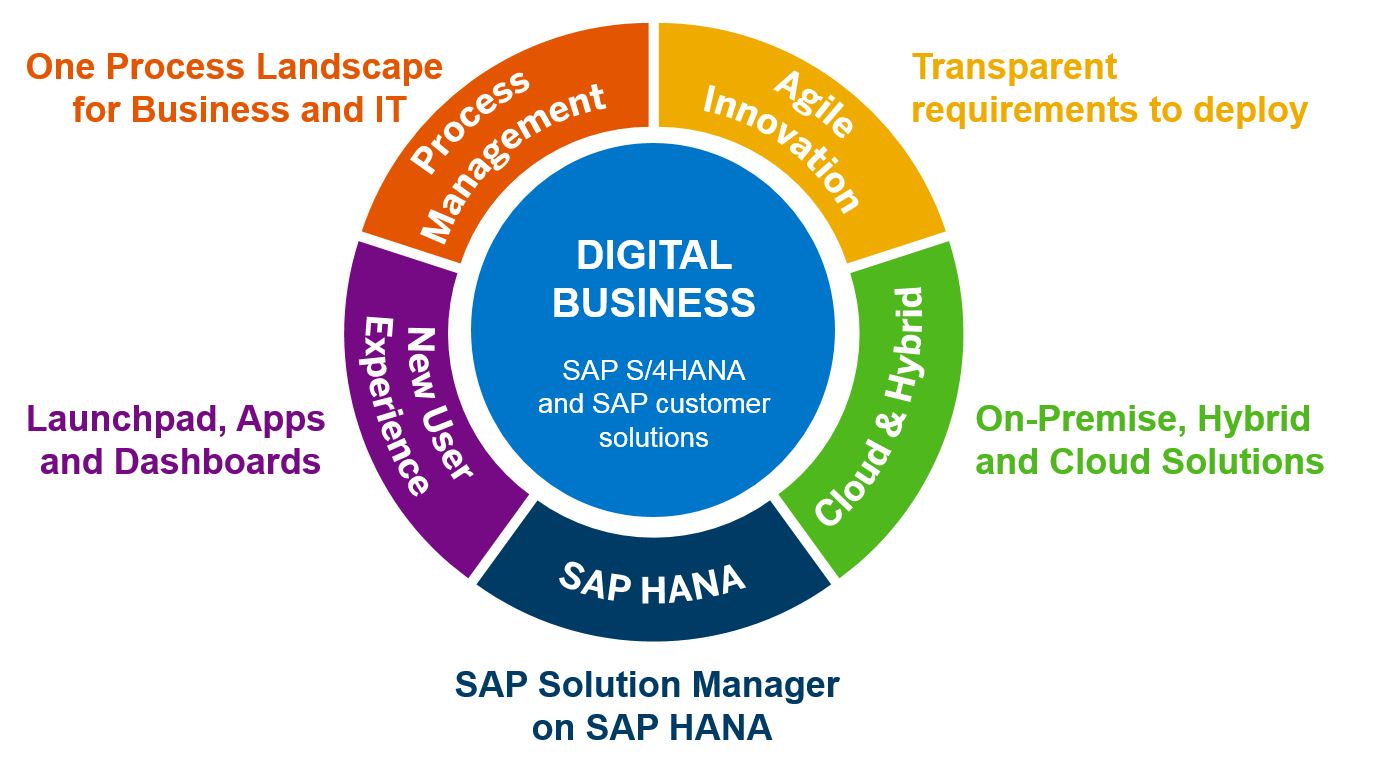
Gearheart will tell you how to build your own search engine if you need an essentially new, “stand-alone” problem-based, individually updated and refreshed IR. Let’s discuss what else your search engine should hold besides document selections and meta-information, such as dictionaries of special terminology, subject area classifiers, resource descriptions, etc.
The Definition
IPS (information retrieval system) is a system that provides search and selection of necessary.
Data in a special database with descriptions of information sources (index) on the basis of the information retrieval language and appropriate search rules.
Why a Search Engine is Needed
The job of a search engine is to find documents that contain either specified keywords, or words that are in some way related to keywords, based on a user’s query. In doing so, the search engine generates a search results page.
Goal for your IPS
The main task of any IPS is to find information relevant to information needs user.
It is very important not to lose anything as a result of the search, that is, to find all documents relevant to the request, and not to find anything unnecessary.
This is why we at Gearheart introduce a qualitative characteristic of the search procedure – relevance.
Relevance
Relevance is the correspondence of search results to the formulated query.
In the following, we will mainly consider the IPN for the World Wide Web (WWW). The main indicators of IPN for the WWW are the spatial scale and specialization.
Spatial scale
IPNs can be divided into local, global, and regional:
- Local search engines may be designed for the rapid retrieval of pages on the scale of a single server.
- Regional IPS describe the information resources of a certain region.
- Global search engines, as opposed to local ones, tend to embrace.
IPNs tools
If possible, to describe the resources of the whole information space of the Internet.
Internet
In general, we can distinguish the following search tools for the WWW: directories search engines, metasearch engines.
Catalog
A search engine with a classified by subject list of abstracts with links to web resources. Classification, as a rule, is carried out by people.
Directory
Search in the directory is very convenient and is carried out by sequentially specifying topics. However, directories support the ability to quickly search for a particular category or page by keywords using a local search engine.
Index
- The reference database (index) of a catalog usually has, limited in size, manually populated by catalog staff. Some directories use automatic updating of the index.
- The result of a catalog search is presented as a list consisting of a brief description (annotation) documents with a hypertext link to the original source.
Search engine
- A search engine has a robot-generated database containing information about information resources.
- A distinctive feature of search engines is the fact that the database containing information about Web-pages, Usenet articles, etc., is formed by a robot program.
- Gearheart highlight, a search in such a system is performed by a user-defined query consisting of a set of keywords or a phrase enclosed in quotation marks. The index is formed and kept up to date indexing robots.
Description
The description of a document most often contains the first few sentences or excerpts from the text document with keywords highlighted. As a rule, the date the document was updated (checked), its. Size in kilobytes, some systems define language and coding.
Results
- What you can do with received results? If the title and description of the document meets your requirements, you can go immediately to its primary source by the link. It is more convenient to do it in a new window, to be able to further analyze the results.
- Many search engines allow you to search for documents, and you can filter your search query by typing additional terms. If the system is very intelligent, you may be offered to search for similar documents. To do so, you select a document you particularly like and specify it to the system as a model to follow.
- However, automating similarity detection is not an easy task and often does not work as well as you hoped. Some search engines allow you to re-sort the results. As a time-saver, you can save your search results as a file on your local disk for later study off-line.
Metasearch engine
Note that different search engines describe different number of sources of information on the Internet. Therefore, you should not limit your search to only one of specified search engines. Now let’s get acquainted with search tools that don’t form their own index, but are able to use the capabilities of other search engines.
These are metasearch engines systems (search services) – systems that can send user queries to multiple search engines simultaneously. Search servers, then combine the results and present them to the user in the form of document with links.
Searching for information sources
Let’s discuss the problem of finding a source of information such as articles in newsgroups.
The tools
- Search tools in this case can be the considered search engines WWW, which index not only the WWW, but also the articles in teleconferences and have a special search mode in teleconferences and have a special search mode specifically for this resource.
- Search in newsgroups, for example, supports search engine Altavista. It should be noted that WWW search engines very quickly index newsgroups and contain information about articles that actually exist on the Web.
- For searching in news archives, there are specialized systems, the best known of which is Deja.
- This system allows both the search for individual articles containing the term entered and the search for specific newsgroups on a specific topic.
- You can register with Deja and subscribe to specific newsgroups.